Danube DeltaMonitoring system and knowledge of sediment flow spilled in the Black Sea
Organization: NIHWM/UDJG (Romania)
In DPS7 the University of Galati intends to prove that using specific equipment for sediment monitoring is possible to improve the knowledge of sediment budget, especially in extreme events, and to obtain a better knowledge of sediment budget transported through the Sulina branch into the Black Sea.
”Dunarea de Jos” University of Galati will be involved in Dalia project in Pilot 7 Danube Delta, Sulina branch, through research about:
- water, sediments, biodiversity;
- developing of prediction models;
- forecasting models based on water quality and sediments;
- developing of a deep-learning.
Within this pilot we will develop new, innovative methods of modelling as machine learning, deep-learning and neural networks in order to establish an analytical framework, suitable to assist environmental management strategies within the Danube River. Thus, in order to achieve this goal, the following activities are considered:
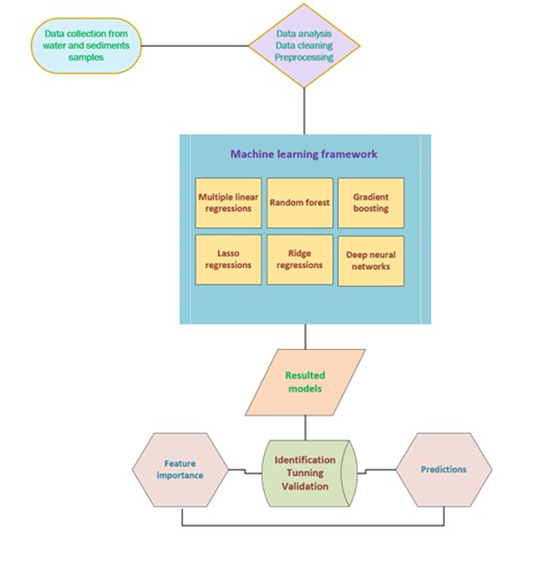
- The developing of prediction models related to both water quality matrix, suspended sediments concentrations and the presence and accumulation of different type of sediments;
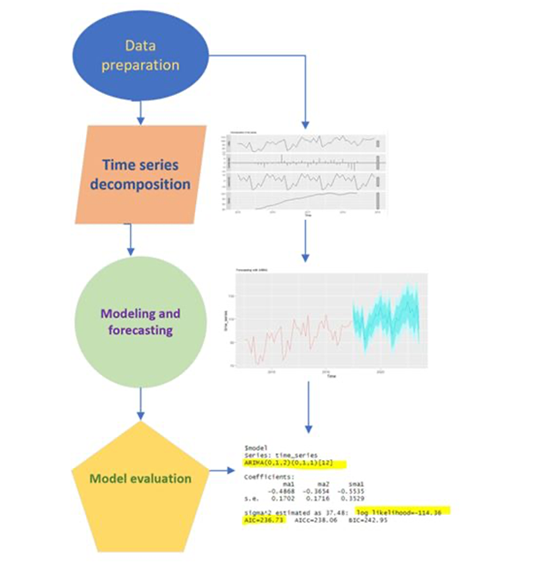
- The developing of forecasting models based on water quality and sediments time series data by using ARIMA;
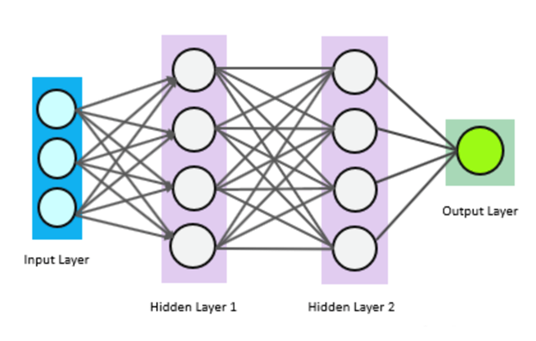
- The developing of a deep-learning based framework, capable of identifying the water quality status, as well as sediments presence and accumulation degree, within the Danube River study sector.
These results will be able to be replicated in all the project Pilots.
The use of new, innovative methods such as machine learning, deep learning and neural networks in order to establish an analytical framework, suitable to assist environmental management strategies within the Danube River is developed based on 3 pillars, as follows:
- The 1st pillar consists of the use of machine learning algorithms for developing virtual sensors for monitoring the quality of water and sediments, based on prediction models.
- The 2nd pillar targets to develop forecasting models, based on water quality and sediments time series data, such as Danube lighthouses for decision management.
- The 3rd pillar establishes a deep-learning-based framework for the identification of water quality and sediment status.




General Overview
The site in question is near the mouth of the Danube into the Black Sea, considered to be a "buffer zone" for the river-delta-sea system (Danube River - Danube Delta - Black Sea). The Danube divides progressively into numerous branches, with the most significant being the Sulina Branch, which is reinforced to allow the navigation of ships and prevent erosion and sediment from being deposited at the entrance of the canal. It is extremely dynamic from a morphological, hydrological, and sedimentological point of view, and is hydrologically monitored by 4 main hydrometric stations. The particularly favorable biological conditions make for the development of vegetation that is specific for the delta, which is declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as a protection zone for habitats and species alike.
Implemented Measures
Water and sediment quality are interrelated and must be taken into consideration to each other to define an appropriate analytical framework that can assist and support decision-making and ensure continuous accurate data. The aim is to develop predictive models related to both water quality matrix and suspended sediment quality, as well as the development of a deep learning (CNN - Convolutional Neural Network) based framework capable of identifying the water quality status as well as the sediment quality status within the Danube River study sector. Lastly, the development of an analytical framework that integrates data provided by partners, related to sediment dynamics, with data related to water and sediment quality, which will continue to be collected by in-situ sampling and sensors, to improve the knowledge of the quantity and quality of sediments discharged into the Black Sea by integrating both numerical and imagery data.
Impact of the Measures on the Environment
The new monitoring system aims to achieve a high economic sustainability solution that will increase the efficiency of the environmental decision-making process in the studied area, and act as a decision support system. Hydromorphology and granulometry data along with the ecological status assessment of the site, will aid in the creation of future action plans and the optimization of different in-situ solutions, but also facilitate the identification and overcoming of possible barriers during the replication activities. Prediction tools will improve the capacity to respond to various future threats and the ability to propose new protection policies that will facilitate and the reduction of chemical and morphological impacts on the Delta.
Summary and Recommendations
Sediment deposition can be altered by both environmental and human factors. The monitoring systems of the outflow of the rivers in the sea can be improved by continuous monitoring with high temporal resolution, to determine the sediment load that has arrived in the sea, with the AI techniques that are used making the system more easily adaptable to other sites. The previous system based on analytical methods is insufficient to provide a holistic picture and assessment of the status of the current situation. The implementation of the new sediment quality monitoring system will engage citizens and stakeholders while adapting timely to the emerging challenges facilitating a mode of frequent evaluation of the actual in-situ situation.
